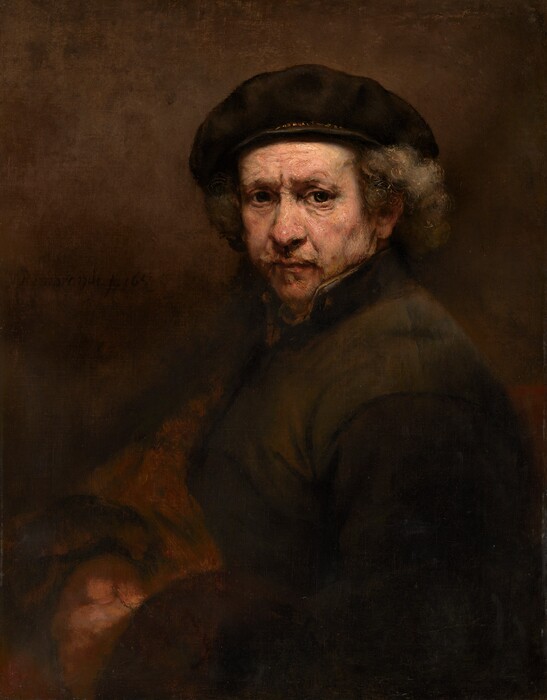
Dutch Paintings of the Seventeenth Century: Self-Portrait, 1659
Publication History
Published online

Entry
The face is familiar, as is the penetrating gaze with which the sitter stares directly out at the viewer. No question, it is Rembrandt, late in his life, at a time when he has suffered through the cruel indignities of failure after so many years of success. Indeed, this portrait, painted in 1659, dates to the year after Rembrandt’s possessions and his house on the Sint-Anthonisbreestraat had been auctioned as a result of his insolvency. It may well have been one of the first works he painted in the small house on the Rozengracht, in the painters’ quarter of Amsterdam, where he had moved when his fortunes and his prospects were at low ebb. In the following year Rembrandt set up a business agreement with his son Titus and Hendrickje Stoffels, the artist’s companion in the last decades of his life, that prevented him from being sued by any of his dissatisfied creditors for recovery of debts.
Rightly or wrongly it seems almost impossible to ponder this work without interpreting it in light of what is known about Rembrandt’s life. This inclination is felt in part because of the extensive biographical information that has come down to us, through which we we are able to feel a closer contact with the man and his life than we do with most artists of this period. It also seems possible to interpret Rembrandt’s mood in such paintings because he painted, drew, and etched so many self-portraits that changes in his appearance can be measured and analyzed by comparing one to another. Even more significantly, however, we read these images biographically because Rembrandt forces us to do so. He looks out at us and confronts us directly. His deep-set eyes peer intently. They appear steady, yet heavy and not without sadness. As Hofstede de Groot remarked in reference to this painting when it was shown in the 1898 Rembrandt exhibition in Amsterdam, “It would be difficult to find in any of his paintings a pair of eyes that peer at us more sharply or penetratingly.” Émile Michel, in his review of the exhibition, was even more expressive about the forcefulness of Rembrandt’s gaze through the heavy wrinkles that had come to age his face so prematurely.
While the observations of Hofstede de Groot and Michel seem entirely appropriate to the image, too often this painting has been subjected to overly romantic interpretations, in which authors have tried to read into this somber image Rembrandt’s own reflections upon the profound tragedy of his life. Interpreting paintings on the basis of an artist’s biography is dangerous, particularly with an artist whose life has been romanticized to the extent that Rembrandt’s has been. In this instance the inclination to interpret this image as a tragic one was reinforced by the thick layers of discolored varnish that had given the portrait a heavy, brooding quality. With the removal of the discolored varnish during restoration in 1992, the fallacy of such interpretations became particularly apparent. With the rich range of pinks and other flesh tones on his face once again visible, Rembrandt’s state of mind seems to have improved remarkably. While the thick impastos and bold strokes he used to model his face still create the dynamic vigor of the head, apparent now as well is the economy with which Rembrandt handled his paint: he has allowed a greenish gray imprimatura layer to read as the shadowed area around the eyes. Finally, the firmness of his touch is accented by the wiry rhythms in his mustache and in the hair protruding from under his beret, which he has delineated by scratching the wet paint with the blunt end of his brush.
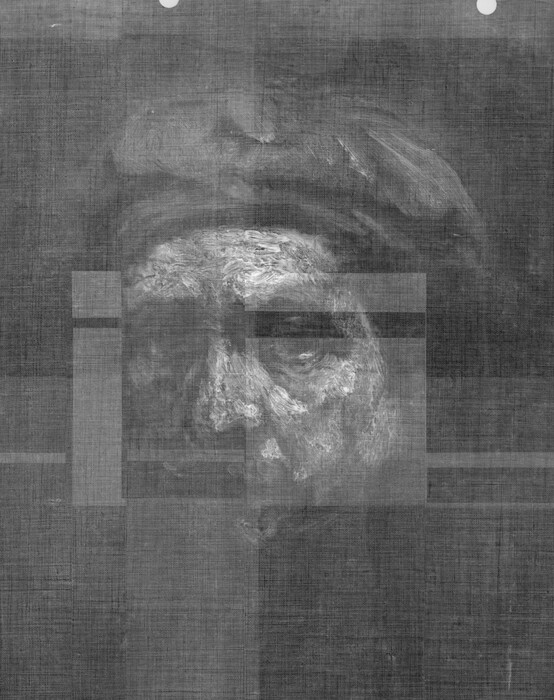
An added benefit from the restoration was the removal of overpaint that had flattened the appearance of Rembrandt’s torso. With the three-dimensional character of this portion of the painting restored, the head seems far more firmly planted on the body than it had previously. The light that so effectively illuminates the head now also accents Rembrandt’s left shoulder and, to a lesser extent, his broadly executed clasped hands. The X-radiograph [see X-radiography] of the head, which reveals the vigorous, almost sculptural character of Rembrandt’s handling of paint, also indicates, through the density of the paint in the beret, that Rembrandt initially painted the beret a different color . It may well have been white, for the upper ridges of a whitish paint layer can be seen through the overlying black paint.
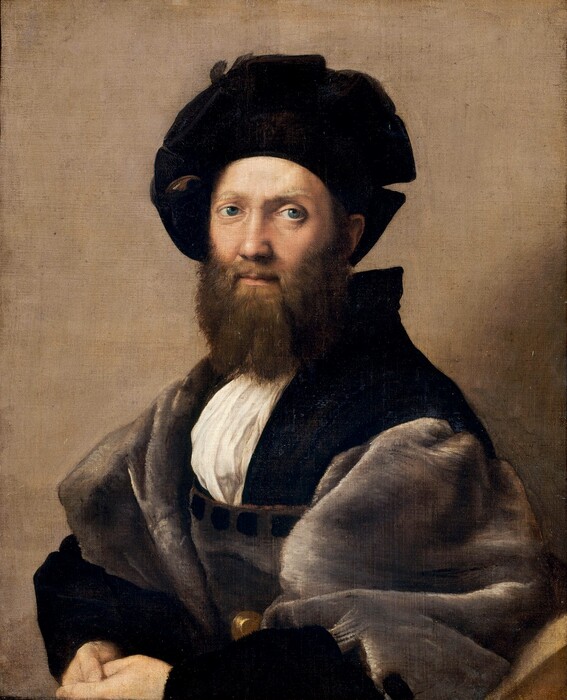
Although Rembrandt’s pose seems so appropriate to the forcefulness of his gaze, quite surprisingly, it was inspired by Raphanel’s portrait of Balthasar Castiglione . The memory of Castiglione’s direct gaze and clasped hands, which Rembrandt first saw when the painting appeared in an auction in Amsterdam on April 19, 1639, must have remained deeply ingrained in his mind for the intervening twenty years. This famous work had made a tremendous impact on Rembrandt, for he even made a rough sketch after it at the sale (Albertina, Vienna). In that same year, 1639, Rembrandt etched a self-portrait that was in part inspired by Raphael’s image and in part by Titian’s portrait, then known as Ariosto, which was in Amsterdam in the Alfonso Lopez Collection (National Gallery, London). In the following year, 1640, Rembrandt painted a self-portrait (National Gallery, London) that reflected in composition and intellectual concept both the Raphael's Balthasar Castiglione and Titian’s Ariosto. In this 1640 Self-Portrait, Rembrandt, dressed in a fanciful historicizing costume, portrayed himself with all of the elegance and dignity of the renowned Renaissance men of letters thought to have been depicted by Raphael and Titian.
In Rembrandt’s 1659 Self-Portrait, all compositional references to Titian’s portrait have disappeared, particularly the stone parapet upon which the artist rests his arm in the 1639 etching and the 1640 painting. Perhaps at this later moment of his life he was drawn to Raphael’s painting because of its self-contained composition, which he must have felt appropriate for expressing the quiet intensity with which he wished to imbue his self-portrait; perhaps he remembered the subdued colors of Castiglione’s costume or the effective way in which Raphael used the beret to frame his head. Clearly Rembrandt has adapted all of these aspects of Raphael’s painting in his self-portrait, while at the same time transforming the nature of his image through dramatic light effects and the rich impastos of his paint.
Most fundamentally, however, Rembrandt returned to Raphael’s prototype because he found in it a vehicle for expressing his perception of himself as a learned painter, a theme that in one way or another underlies a number of his late self-portraits, particularly his magnificent paintings in the Frick Collection, c. 1658, and in the Iveagh Bequest, Kenwood, c. 1665. In all three of these works Rembrandt projects a strikingly positive self-image, in which allusions to his self-esteem as an artist are conveyed through pose, costume, and expression.
Technical Summary
The original support, a tightly, plain-woven fabric with fine threads, has been lined. The tacking margins have been removed and a coating of white lead has been applied to the back of the lining. The double ground consists of a thick, reddish brown lower layer and a very thin, light gray layer.[1] The design was then sketched in a transparent brown underpaint layer intentionally left visible in the proper right sleeve and in the nostrils, mouth, and neck bordering the collar. The exposed areas of the brown sketch are abraded, which has diminished their significance.
The figure was painted with opaque, broad, flat brushstrokes, while the background and hands were thinly painted. The hair has been articulated by fine brushstrokes and lines incised with the butt end of a brush into the still-wet paint. The highlights of the face were first created overall with heavy short strokes of richly impasted paint, with individual brushstrokes swirled wet-into-wet rather than blended. Once dry, the paint was reworked with unblended, short, distinct strokes of darker colors following the initial brushwork pattern. These were softened with half-shadow mid-tones. Strokes of white paint under the beret indicate that Rembrandt initially planned a lighter color beret than the present black one.
While the face and hands are largely intact, much of the figure and the background at the left have suffered from abrasion. The painting underwent treatment in 1992 to remove discolored varnish and overpaint. The blackish paint to the left of the figure and a patchy semi-opaque coating, applied in a prior restoration to disguise abrasion, were left in place.
[1] Cross-sections were analyzed by the Scientific Research department (see report dated November 13, 1992, in NGA Conservation files).